Osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease of the cartilaginous structures of the spine, leading to a violation of the structure and functional characteristics of the intervertebral discs and the surrounding musculoskeletal system. Depending on the location, there are three main types of osteochondrosis:

- cervical;
- chest;
- lumbar.
According to the statistics of the World Health Organization, this disease affects from 50% to 90% of the world's population. It is noted that in recent years, osteochondrosis is rapidly growing younger. With a detailed examination, today it will be difficult to find a person over 20 years old without disc protrusions and other primary signs of this disease, and the average age of the onset of full-fledged clinical signs (chronic pain, posture disorders, etc. ) is 30-36 years.
Causes of osteochondrosis
The main causes of osteochondrosis of the spine include:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hereditary predisposition;
- metabolic and gastrointestinal disorders that interfere with the normal absorption of essential nutrients by the body;
- occupational risks, most often exposure to vibration;
- development of scoliosis and various types of posture disorders during active growth of the body;
- insufficient water intake, permanent dehydration;
- metabolic disorders, malnutrition and lack of essential nutrients in the diet;
- violation of calcium metabolism in the body;
- increased physical activity and traumatic sports;
- uncomfortable shoes;
- chronic stress;
- trauma;
- congenital anomalies in the development of the musculoskeletal system.
Most often, this is the fault of the lifestyle that most modern people lead and the very nature of the disease. Osteochondrosis is called the payment of a person for walking upright.
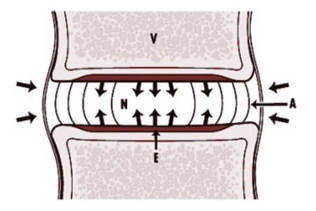
Unfortunately, nature has not yet developed a reliable mechanism of protection against the negative effects of vertical pressure. When running, jumping and other mounting loads, our discs contract and expand under the influence of the vertebrae, acting as a shock absorber. In such a situation, the cartilage tissue undergoes constant microtraumatization. Gradually, there are more such microtraumas, and if at a young age the body's reserves are enough to patch and restore them, then after 21 years these processes are sharply inhibited, and from the age of 25 they completely decline, the processes of degeneration begin to prevail over the processes of regeneration.
Due to lack of movement, uncomfortable sitting postures, bad habits, lack of sleep, insufficient rest, stress, the work of blood vessels deteriorates, nutrients begin to flow less, the nutritional processes of the discs begin to be disrupted. Eventually, this causes the cartilage to wear out.
Genetic predisposition also plays an important role in the rate of development of osteochondrosis. One of the main factors in the progression of the disease are deviations in the synthesis of connective tissue. Sometimes these failures occur in the course of life and are caused by lifestyle and age factors, but more often our genes are to blame.
Exactly also the likelihood of the disease may depend on how at the genetic level are susceptible to various ailments and other structures of the human body, on which the work and nutrition of the spine as a whole depends.
Mechanism of osteochondrosis development
The intervertebral disc is an elastic gelatinous body. Like any cartilaginous tissue, it contains special substances - mucopolysaccharides. During physical activity, metabolism in the body of the disc increases and more nutrients begin to flow to it. The number of incoming enzymes increases, which change the properties of mucopolysaccharides. They begin to attract more water from the intercellular space, the disc begins to swell, compensating for the load on the vertebrae. The process of binding water continues until the pressure on the disk comes to equilibrium. When the load is removed, the process is reversed. The water returns back, the elasticity of the disk body decreases, and dynamic equilibrium is restored.
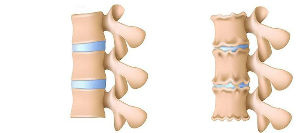
With osteochondrosis, changes in the body of the intervertebral disc first of all occur. The amount and composition of mucopolysaccharides changes, the content of chondroitin sulfates and hyaluronic acid may decrease. As a result, all this leads to dehydration of the nucleus pulposus. The disc loses its elasticity, decreases in volume and can no longer normally withstand the load acting on it. The nucleus pulposus also begins to lose elasticity.
The changes occurring lead to a violation of the shock-absorbing properties of the disc, which negatively affects its fixing ability. During movement or exertion, some parts of the spine, albeit insignificantly, can shift relative to each other. At first, weakened fixation can be compensated for by the strength of the muscles and ligaments. However, in the future, under the influence of various kinds of negative factors (prolonged stay in a fixed vertical position, posture disorders, heavy physical exertion), pathological changes or atrophy of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus may occur. The opposite process can also occur - an excessive increase in muscle fixation. The muscle groups responsible for fixing the spine become overly tense, and this state does not go away even during rest.
Due to uneven load distribution, sprains, muscle weakness, progressive degenerative changes in the discs, changes begin to occur in the bone tissues of the surrounding vertebrae. The density of bone structures begins to increase, due to the fact that the body begins to pump calcium there in order to compensate for the pressure that the disc previously took on itself during loads.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
The primary diagnosis is made on the basis of complaints and preliminary examination of the patient. A check is made for the presence of pain in various parts of the spine under conditions of rest and movement. The doctor determines the localization of pain, its duration, specifies the factors that provoke pain, in which cases the pain intensifies and decreases. It is specified for how long the disease has lasted, what contributed to its onset, how it proceeded, under what circumstances the exacerbation occurs, how the patient feels during remission.
Next, the degree of spinal lesion is determined. Possible range of motion is set:
- tilted (forward, backward, sideways);
- rotational movements in different parts of the spine.
It is necessary to pay attention to the physiological curves of the spine, possible flattening (in rare cases, strengthening) of lordosis in the lumbosacral and cervical regions. Possible presence of possible spinal deformities is revealed:
- scoliosis;
- involuntary tilt of the head to the painful side;
- oblique pelvic position.
Potential sensitivity violations are determined. The state of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus is assessed, a possible decrease in tone and muscle atrophy.
X-RAY
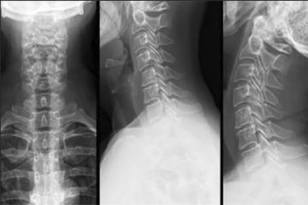
X-ray examination allows to assess the condition of the affected vertebrae and discs. The picture can be taken in 2 mutually perpendicular planes - straight and lateral, as well as in two oblique projections. X-rays are performed while standing or lying down. If necessary, the x-ray can be performed in the flexion-extension position, as well as with a tilt to the side.
MRI (MAGNETIC RESONANCE TOMOGRAPHY)
The most informative method for diagnosing osteochondrosis. In addition to bone structures, it can also assess the condition of the soft tissues surrounding the spine (cartilage, blood vessels, muscles, ligaments, nerves, etc. ). MRI can be performed in three projections. Unlike tomography, it does not expose the body to X-rays.
CT (COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHY)
Has several advantages over X-ray examination. X-ray shows better changes in the bone structures of the vertebrae, the height of the disc, the emerging osteophytes and bone growths, the presence of subchondral sclerosis. However, CT allows you to see possible ruptures of the discs, compression of the roots, changes in the dura mater of the bone marrow.
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG)
EMG is an assessment of the bioelectric potentials of the muscles of the spine, which arise when they are excited. In fact, it is a method of recording the electrical activity of muscle fibers. Promotes a more objective diagnosis of osteochondrosis, as well as control over the course and prognosis of the disease.
RHEOGRAPHY
Serves to study the state of the vessels of the extremities, brain and back in case of lesions of certain parts of the spine.
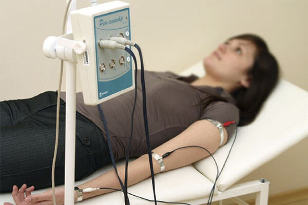
Rheovasography (RVG) is a type of rheography performed when examining the vessels of the arms and legs. With radicular syndrome, there are spastic phenomena in the arteries of the upper and lower extremities, mainly from the side of the lesion. RVG allows you to identify them.
Rheography is especially informative for various vascular events in the affected area of the spine, especially in the syndrome of a compressed artery. This research method allows you to indirectly judge the state of the affected vertebra and track the dynamics of the disease.
ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY (EEG)
Study of the biopotentials of the brain in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. EEG is most informative when performing tests for head rotation and neck extension. Allows you to identify abnormalities in the vertebral arteries, which lead to a violation of the blood supply to the brain. The study evaluates the rhythm, frequency and amplitude of waves. Arterial lesions are manifested by flattening and desynchronization of the encephalogram. In severe cases, the rhythm may be poorly expressed or absent altogether. There may also be a number of other pathological phenomena that a specialist can decipher.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
Treatment of diseases always requires an integrated approach. Depending on the severity and severity of manifestations, the course of intensive therapy can last from 1 to 3 months, and additional prophylaxis aimed at consolidating the result obtained up to 1 year.
Treatment can be carried out in 2 directions: conservative and operative.
CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT FOR OSTEOCHONDROSIS
This type of therapy is aimed at relieving pain, increasing the healthy range of motion of the spine and preventing further development of the disease. Includes the following directions:
- Drug therapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Exercise therapy (physiotherapy exercises);
- Massage;
- Manual therapy;
- Osteopathy;
- Innovative techniques (stem cells);
- Psychological rehabilitation;
MEDICAL THERAPY
If the pain syndrome is pronounced and significantly worsens the quality of life, then the use of nerve blockade is recommended. Blockades are divided into the following types:
- Blockade of trigger points (muscle seals formed as a result of uneven distribution of the load on the back muscles);
- Intraosseous - injection of anesthetic into the corpus spongiosum to relieve pain and treat concomitant neuralgic, motor and vascular disorders;
- Facet - injection of anesthetic to reduce pain in nerve roots and facet joints;
- Paravertebral - the introduction of drugs into the spine in the places where the nerve roots come out, in order to temporarily disable the pain reflex;
- Epidural - injection of a drug into the epidural space of the lumbosacral spine with radicular syndrome in order to relieve pain;
Groups of drugs used for the treatment of osteochondrosis:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - used to stop inflammatory processes;
- Antispasmodics - to relieve spasm;
- Antioxidants - to prevent the effects of free radicals that accelerate aging and the development of degenerative processes in tissues;
- Preparations for improving blood circulation in the spine;
- Chondroprotectors - for the regeneration and inhibition of the processes of degeneration of cartilage tissue.
Chondroprotectors are an integral part of the therapeutic treatment of osteochondrosis. They are available in three forms: injectable, tablet, as well as ointments and creams.
Medicines can be prescribed for external use in the form of ointments and gels, for intramuscular injection in the form of injections, and orally in the form of capsules and tablets.
Medication is exclusively prescribed by a physician. In the absence of pain and pronounced degenerative changes, the use of medications is not justified. Treatment of osteochondrosis is impossible exclusively with the help of medicines. Therapy should include diet, optimal physical activity, physiotherapy, if possible, psychological rehabilitation and other preventive measures.
MASSAGE FOR PREVENTION OF OSTEOCHONDROSIS
The benefits of massage are as follows:
- improvement of blood circulation, stabilization of metabolic processes of the intervertebral disc and surrounding tissues;
- removal of muscle-ligamentous spasms;
- strengthening the muscles and relieving stress from the spine;
- inhibition and prevention of the development of inflammatory processes;
- increasing the tone and increasing the efficiency of the body as a whole.
PHYSIOTHERAPY
Physiotherapy in the treatment of osteochondrosis, depending on the stage of the disease and the patient's condition, is used both in combination with drug therapy, or separately.
For degenerative diseases of the spine, depending on the symptoms and type of manifestations of the disease, the following types of physiotherapy are used.
UV (LOCAL ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION)
Direct exposure to UV light on the skin stimulates the production of vitamin D, which plays a key role in the absorption of calcium. The procedure is performed using radiation, which has a bactericidal, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
ULTRASONIC.
Exposure of body tissues to high-frequency sound radiation (from 20 Hz and more). They are used in combination with various anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs for external use for their better penetration into body tissues. The main purpose of the method is to eliminate pain syndrome of various localization.
SHOCK WAVE THERAPY
The essence of the procedure is to transmit an acoustic wave to the site of pain. The main goal is to relieve pain, improve blood microcirculation, accelerate metabolism.
LASER THERAPY
Impact with special helium-neon lasers. Such radiation promotes the activation of bioelectrical processes in nerve tissues and has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. The laser is applied to the inflamed spinal nerve roots located near the affected area of the spine.
MAGNETOTHERAPY
Exposure to the affected area of the spine with a magnetic field, as a result, a bioelectric field is created in the tissues, which stimulates all metabolic processes in the affected area at the cellular level. The magnet has an anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effect.
ELECTROPHORESIS
Exposing the affected area to a weak electric shock. Under the influence of an electric field, particles of a dispersed medium are able to easily move in gaseous and liquid media. In this way, the necessary drugs can be delivered directly to the affected area, which significantly increases the effectiveness of treatment.
BALNEOTHERAPY
Methods for the treatment of osteochondrosis with the use of various kinds of mineral waters: baths, showers, pools. During the procedure, mineral particles penetrate the skin and affect the nerve centers.
MUD
Treatment of osteochondrosis with mud is used in the form of mud applications (wraps). The impact on the body occurs through the influence of high temperatures in combination with the chemical composition of the mud. In the affected tissues, metabolism is accelerated, blood circulation is improved, an anti-inflammatory effect is exerted, and the severity of pain syndrome decreases.
TRACTION THERAPY (SPINE LENGTH)
One of the most effective treatments for osteochondrosis. During stretching, stretching of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the spine occurs, the distance between the vertebrae increases by 2-4 mm. Possible hernias and protrusions are reduced. Excessive pressure on the nerve roots and blood vessels is relieved, which can be hernias and osteophytes (bone growths on the vertebrae). Spinal traction also helps to reduce local edema, improve blood circulation, and relieve excessive tension of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus.
VACUUM MASSAGE
The procedure is performed using medical cups or a special apparatus. During vacuum therapy, the blood vessels of the internal organs are stimulated. In places where the massage was carried out, the production of enzymes, biologically active substances, accelerating internal metabolism and regeneration processes is activated. With continued use, the procedure can replace significant tissue rejuvenation at the site of application.
CRYOTHERAPY
Sharp short-term cooling of the body to critically low temperatures, which has a therapeutic effect. It is characterized by high efficiency in suppressing pain syndrome, since a sharp drop in temperature blocks pain receptors, significantly increasing the pain threshold. It has an excellent anti-inflammatory effect. There is a decrease in the level of collagenase (an enzyme that breaks down peptide bonds in all types of collagen). The formation of granulomas is blocked. Edema of soft tissues and lymph nodes is removed, lymph flow returns to normal.
Exercise therapy - THERAPEUTIC EXERCISE FOR OSTEOCHONDROSIS
The main task of exercise therapy is to relieve and strengthen the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the spine, to increase the flexibility and range of motion of the vertebrae. Exercise for osteochondrosis helps to improve blood circulation and increase the permeability of the tissues surrounding the spine for better permeability of nutrients.
Basic principles of physiotherapy exercises for any type of osteochondrosis
- Classes should take place in a well-ventilated area, preferably outdoors;
- Exercise should only be performed during remission, when symptoms are absent;
- Clothing should be as loose as possible and not restrict movement;
- All movements should be performed smoothly, and the amplitude and number of repetitions should increase gradually;
- Stop exercising immediately if pain occurs;
- A lot depends on the breath, try to listen to it as you practice. All stretching exercises should be done on exhalation;
- Be sure to monitor your heart rate and blood pressure. If these indicators exceed the norm, reduce the intensity of the load;
- In any wellness practice, consistency plays an important role; for the fastest achievement of the result, observe regularity in your classes;
- "Less is better, but more often. "Keep the exercise at a low intensity, but ideally if you can do the gymnastics several times a day. Try to find time for a little gym even at work.
- The set of exercises in each case is selected individually, before starting classes, be sure to consult your doctor.
WHAT TO DO IF THE TIME IS NOT ENOUGH TO PERFORM THE EXERCISES?
If you do not have enough time to do full-fledged exercises for the prevention of osteochondrosis, we offer you five-minute complexes that can be performed outside the home (for example, at work).
MANUAL THERAPY FOR OSTEOCHONDROSIS
Manual therapy is a local dosed physical effect on the affected area of the spine and surrounding tissues. Its goal is to restore the normal functioning and mobility of the vertebral segments in the damaged areas.
It is considered one of the most effective and gentle methods of treating osteochondrosis, especially in the initial stages.
As a rule, the procedure includes 3 components:
- Relaxation massage - warming up and warming up muscles, removing excessive tone;
- Mobilization - the use of relaxing techniques and stretching to relieve spasms and improve the motor characteristics of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus and joints. The goal is to normalize movements, improve blood circulation, restore metabolism in areas affected by osteochondrosis. Can be performed in passive technique or by traction;
- Manipulation - forced actions carried out with the aim of returning the vertebrae to their places and restoring the normal functioning of the joints.
INDICATIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS FOR MANUAL THERAPY
Manual therapy has a number of limitations, which are determined by the patient's condition.
Reading:
- widespread osteochondrosis with large-scale lesions of the spinal column;
- early stages of disease with localized lesion;
- functional blockade of vertebral joints of the second and third degree;
- spinal hernia.
Contraindications:
- tumors of the spine and paravertebral structures;
- tuberculosis;
- ankylosing spondylitis;
- trauma and postoperative period;
- grade 3-4 vertebral instability;
- inflammation of the spinal cord and its membranes;
- disorders of cerebrospinal circulation;
- pronounced pain syndromes;
- tears and severe sprains of muscles and ligaments;
- dysfunction of nerve roots;
- spinal fractures;
- and others
TREATMENT PERIOD
Depending on the characteristics of the course of the disease, the duration of treatment can range from 1-2 weeks to 2-3 months. The number of procedures depends on the characteristics of the patient and a number of related factors.
































