The first symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis usually do not bother a person. The reason for the heaviness in the back of the head and tingling in the neck area can be common fatigue or colds. But if the disease is not diagnosed in a timely manner, this can lead to adverse consequences. The neck is one of the most mobile, but not strengthened by muscles, parts of the body. Even strong head rotation or sudden movements can harm the spinal discs and become a predisposing factor in the development of pathology. Therefore, you need to know the causes and symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis, as well as ways to treat it, so as not to face this problem in the future.
Description of the disease
Cervical osteochondrosis is a disease resulting in degenerative disorders of the intervertebral discs in the neck. Vertebrae, soft and cartilaginous tissue are destroyed. It is the neck area that is prone to injury, because this part is the most mobile, but has a weak muscle corset.
The whole body puts a lot of stress on the small vertebrae, which are very close to each other, as well as close to the arteries that supply the human brain. Therefore, there is a displacement of the vertebrae, which leads to compression of the nerves and blood vessels. Compression can displace the discs, causing herniated discs.
Osteochondrosis most often affects able-bodied people aged 30 to 40 years. This is due to the massive decline in the physical activity of the population.
Causes of development and risk factors
The main reason for the development of cervical osteochondrosis is a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle, static loads, leading not only to the development of osteochondrosis, but also to the appearance of pain in the back. Stress associated with carrying and lifting weights, sharp bending and extension, and turns can also cause osteochondrosis. Other causes of cervical osteochondrosis include:
- inheritance;
- overweight;
- unhealthy diet (lack of vitamins, minerals and fluids in the body);
- nervous tension, frequent stress;
- hypothermia;
- incorrect body position during sleep, using uncomfortable pillows;
- trauma, bruises in the occiput and neck;
- systemic diseases leading to degenerative changes in cartilage tissue;
- congenital pathologies of the structure of the spine.
Hormonal imbalance, hereditary predisposition, rheumatism, hypothermia, various injuries of the cervical spine are risk factors that can cause the development of not only this disease, but also intervertebral osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
Why is cervical osteochondrosis dangerous?
Cervical osteochondrosis is one of the most dangerous diseases of the spine, along with intervertebral osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, because in the neck area there are many vessels, capillaries and the main vertebral artery that feeds the brain. That is why the unpleasant consequences of this disease include:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- brain oxygen starvation;
- hypertension;
- ischemia;
- spinal stroke;
- impaired vision, hearing, coordination of movements;
- frequent dizziness;
- intervertebral hernia, protrusion, leading to disability;
- fainting;
- jumps in blood pressure;
- heaviness in the occiput;
- fatigue;
- a feeling of stuffy ears.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is dangerous because it is difficult to detect at the initial stage, since the disease is not accompanied by severe symptoms. With obvious symptoms, it is also difficult to diagnose the disease, because when the vessels and nerves are squeezed, signs similar to angina pectoris appear.
Symptoms by severity
Depending on the severity of the disease, there are 4 degrees of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Each stage of the disease has its own symptoms.
First degree
The disease is at its initial stage during the period of degeneration of cartilaginous tissues. It has the following symptoms:
- slight pain in the neck, shoulders and arms;
- headaches;
- minor neck stiffness;
- decreased sensitivity of the skin of the collar zone.
Bending and turning the head aggravates all of these symptoms. At the initial stage of the disease, patients rarely go to the doctor, since they consider these signs to be a consequence of fatigue, lack of sleep and changes in weather conditions.
Second degree
At this stage, the patient may complain of pain not only in the neck, but also in the upper limbs. Is accompanied by the following symptoms:

- short-term loss of sensation in the skin in the shoulders and arms;
- persistent headaches;
- visual impairment;
- malaise, weakness in the arms;
- decreased tendon reflexes;
- pain under the scapula;
- sleep disturbance.
When the head is held in the same position for a long time, the person experiences severe pain. At this stage, it is best for the patient to see a doctor in order to establish a diagnosis and initiate treatment.
Third degree
Pain at this stage almost does not stop and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- collar and heart pains;
- frequent herniated discs;
- complete loss of sensation in the upper limbs;
- decreased mobility of the cervical spine.
Most often, when diagnosing osteochondrosis at this severity, they begin to carry out active medication and physiotherapy.
Fourth degree
This is a very severe stage of the disease. At this stage, the intervertebral disc practically collapses, in the place of which bone growths appear - osteophytes, signs of cervical spondylosis, pinching the nerves, which leads to a worsening of the patient's condition and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the neck, heart;
- curvature of the spine;
- appearance of a hernia in the cervical spine;
- tendon reflexes disappear completely;
- paralysis and paresis of the muscles of the arms and shoulders.
At this stage, the patient is unable to support his head on his own, urgent hospitalization is required.
When the arteries are compressed, such a serious complication as spinal stroke occurs, which leads to ischemia of certain parts of the brain.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis plays an important role, because all therapeutic therapy depends on it. The disease is diagnosed by its symptomatic manifestations. The main diagnostic steps are:
- Taking anamnesis. The doctor reads the patient's medical history. During the conversation, he learns how the disease proceeds, its symptoms. The doctor must figure out if any treatment was carried out and how effective it was. The specialist should know about hereditary factors, about the bad habits of the patient, as well as about the conditions of the place of work.
- Examination of the patient. The doctor examines the patient and finds out how the disease manifests itself. Examines the neck, its position relative to the body, difficulty in movement. Be sure to inspect the skin to see if there have been any changes. Feels the neck area and determines if there are lumps. Sensitivity is checked with a needle (tingling).
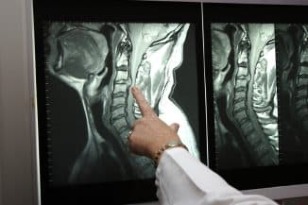
- Radiography. This study is carried out for accurate information about the condition of the spine and cervical spine. Pictures are taken so that it can be seen directly and from the side. Sometimes the patient is asked to rotate the neck to take a functional X-ray. Due to the X-ray, it is possible to find out how mobile the damaged vertebrae are, their displacement, salt deposition and the presence of seals.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. MRI is one of the most effective methods for diagnosing osteochondrosis of the neck. This procedure is painless and accurate enough. As a result of the creation of a magnetic field, it is possible to identify not only the disease itself, but also to determine the severity. This makes it possible to find an effective treatment.
- Computed tomography. Diagnostics is carried out using X-ray irradiation. The patient is placed in a tomograph, which can be closed or open. Next, scanning takes place, and the information goes to the computer, after which it is processed. These images make it possible to determine the exact picture of the disease.
It is imperative to diagnose cervical osteochondrosis. Only thanks to such methods it is possible to determine all disorders in the body. Do not self-medicate, as it can lead to undesirable and dangerous consequences.
Treatment details
The type of treatment directly depends on the degree of osteochondrosis and the individual parameters of the patient. Some procedures can improve the patient's condition only in the initial stages of the disease, and when the condition is neglected, more radical methods are required.
Medication
The choice of one or another drug for osteochondrosis depends on the purpose of its use. There are several groups of medicines:
- Stopping tissue deformation - chondroprotectors.
- Improvement of microcirculation.
- Vitamin complexes, especially B1, B6, A, C.
- Pain relief - analgesics of various nature.
- Anti-inflammatory.
The correct use of the right medication will help restore the mobility of the neck and upper limbs, as well as keep the bones from further deformity.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy as a method of treatment aims to:
- reduce pain;
- stop inflammation;
- relieve muscle spasms;
- normalize metabolism;
- restore blood circulation;
- relieve pressure of osteophytes on nerve fibers.
There are several types of physiotherapy:
- Magnetotherapy. During the procedure, the focus of the disease is affected by variable or constant magnetic fields of various frequencies. A special device is used - a magnetophore, which can be purchased and used independently. A session lasts no more than 20 minutes;
- Electrotherapy. The most common treatment for osteochondrosis. The electric current increases blood circulation in the tissues, which helps to speed up treatment and reduce pain. Do not use by people with metal medical devices, such as a pacemaker;
- Laser therapy. It is carried out with the help of helium-neon lasers, which act on the nervous tissue, relieving inflammation of the nerve roots. The method appeared recently, but is already considered an effective method of treatment and pain relief;
- Balneotherapy. It consists in treatment with mineral waters and taking mud baths. Salts, trace elements and other bioactive components of water penetrate the skin, affecting the centers of the nervous system and sensitive endings;
- Shockwave therapy. During the procedure, an acoustic wave is directed to the deformed cervical spine, which improves the transport of biological fluids and reduces pain.
Physiotherapy procedures for cervical osteochondrosis allow you to act on problem areas without the risk of complications. They are acceptable at any age, but they are not applied on their own, but are an addition to the main treatment.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy for cervical osteochondrosis will help not only improve physical condition, but also prevent possible exacerbation of the disease. You can also increase the sensitivity of your upper limbs and neck with regular exercise. The following exercises are helpful for sickness:
- turns and tilts of the head;
- raising the head while lying on the back and on the side;
- pressing in the temple area, resist with the head;
- stretching neck muscles;
- hand rotation.
Each exercise is performed not abruptly, at a slow pace, 5-8 times in a sitting position. Do not perform with the maximum amplitude, so as not to worsen the state of health and not cause dizziness. Exercises should be performed under the supervision of an instructor or a treating specialist who will demonstrate the correct implementation of the complex.
Extension
Traction in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine occurs under the weight of your own body. The procedure relieves back pain, neck pain and curvature of the spine. The stretching is carried out using a traction, which varies in duration. Thanks to this, muscle spasm is relieved, the vertebrae fall into place, which makes it possible to stretch the spinal column and hold it in this position. There are two methods of traction in medicine:
- dry;
- underwater.
Dry cervical traction of the spine is carried out using special medical traction tables or couches. Such machines make it possible to evenly apply the load on the spine without causing any harm.
The underwater hood is becoming more and more popular due to its simplicity and efficiency. In this case, the procedure is carried out under the influence of water, the temperature of which is 36-37 degrees, which has a positive effect on the muscles and its tone. Underwater traction reduces pain, improves blood circulation and relieves vasospasm.
Cervical spine traction should be performed in a hospital under the strict supervision of a physician. Self-treatment at home can lead to complications and injury.
Trench Collar
The Schanz Collar is an orthopedic splint that is applied to the neck and helps to fix the cervical vertebrae, preventing them from moving and causing pain. In this way the weight of the head does not load the spine, but is distributed to the shoulder muscles.
The collar is made from hard materials but has soft edges. It must be selected strictly according to the parameters:
- at the back, the collar should touch the back of the head, and below the base of the neck;
- the size should not exceed the length of the neck;
- after putting on the neck is immobilized, while the patient does not experience pain.
In case of minor damage to the cervical vertebrae, the collar should be worn only for 1 hour, 2 times a day. It does not hinder body movements, so you can do your usual activities in it. It is forbidden to lie down. This can damage the cervical spine due to pressure on it.
Needle Applicator and Lyapko
One of the ways to treat osteochondrosis was the invention of the music teacher's needle applicator in the 80s of the last century.
A needle applicator is a small rubber or fabric mat on which square or round plates are attached. They have plastic blunt polystyrene spikes. A few years later, the Ukrainian reflexologist Mykola Lyapko improved the invention and created his own applicator. It is considered the most effective because it is made of medical rubber with games attached to the top.
The creator of the needle applicator, having received serious burns, decided to cure himself. He attached sharp pins to a rubber mat and used it to heal wounds.
Traditional methods
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the neck is very effective with folk remedies. Each folk remedy is associated with warming up the affected area.
Folk remedies include:
- warming compresses;
- herbal ointments
Medical compress is a common method of treating osteochondrosis. There are many recipes for warming compresses. Some of them are:
There are many recipes for warming compresses. Some of them are:
- Take half a liter of vodka and dissolve 1 g of propolis, 50 g of aloe and mustard powder. Soak a piece of gauze with the prepared solution and put it on the neck, wrapping it in a warm scarf. Make a compress at night.
- Grate two potatoes and mix with two tablespoons of honey, preheating in a water bath. Lubricate the neck with the mixture, close it with plastic and wrap it in a scarf. You need to withstand the compress for 3-4 hours.
Herbal ointments such as ginger are also effective. For her you need ginger juice and calendula tincture. Mix the components in equal proportions and rub the sore spots with the prepared mixture. Ginger will improve blood circulation, and calendula will relieve inflammation. Traditional medicine recipes can significantly improve the patient's condition, but they will not completely eliminate the problem.
Surgery
An operation on the cervical spine for osteochondrosis can be prescribed if there are some complications: intervertebral hernias, narrowing of the spinal canal or spinal cord disorders. In this case, surgical intervention is urgent and urgent. If necessary, the damaged intervertebral disc is removed, and an implant reinforced with a titanium plate is placed in its place.
Titanium plates, despite their lightness, are very durable. They restore the integrity of the bone and are a guarantee that osteochondrosis in this area will no longer occur.
Nutrition and Diet
In case of osteochondrosis, it is necessary to ensure the intake of glycosaminoglycans in the body, which are needed for the formation of cartilage tissue. These compounds are found in jellied fish, jellied meat, and jelly. In addition, the following products are useful for disease:
- meat and fish dishes, nuts, beans (high in protein);
- dairy products (cheese, cottage cheese) will enrich the body with calcium;
- green vegetables, seeds support magnesium levels;
- olive oil instead of sunflower oil.
In case of osteochondrosis, you need to refuse such food:
- salt and sugar;
- semi-finished products;
- spicy and fatty foods;
- coffee;
- high-calorie foods.
When compiling a diet, be sure to include foods high in vitamin A (eggs, carrots), vitamin C (citrus fruits), and B vitamins (red meat, seafood).
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at preventing the development of osteochondrosis. They are quite simple:
- engage in physical activity (walking, swimming, running);
- strengthen the neck-collar area;
- sleep on a flat and hard bed on a small pillow;
- balance your diet;
- see a doctor periodically.
It is especially important to observe and maintain prophylaxis after a cured disease, as there is a possibility of relapse if the load on the neck is not observed.
Conclusions
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine arises from a strong load on a weak muscle corset. This can be facilitated by physical inactivity, improper posture during sleep, and a number of other factors.
- The main danger of osteochondrosis is that important blood vessels and arteries that feed the brain can be damaged.
- Treatment is prescribed by a doctor. An integrated approach is effective, which includes taking medications, physiotherapy, gymnastics, dieting and other procedures.
- Radical method - surgery is used only if there are complications.
































